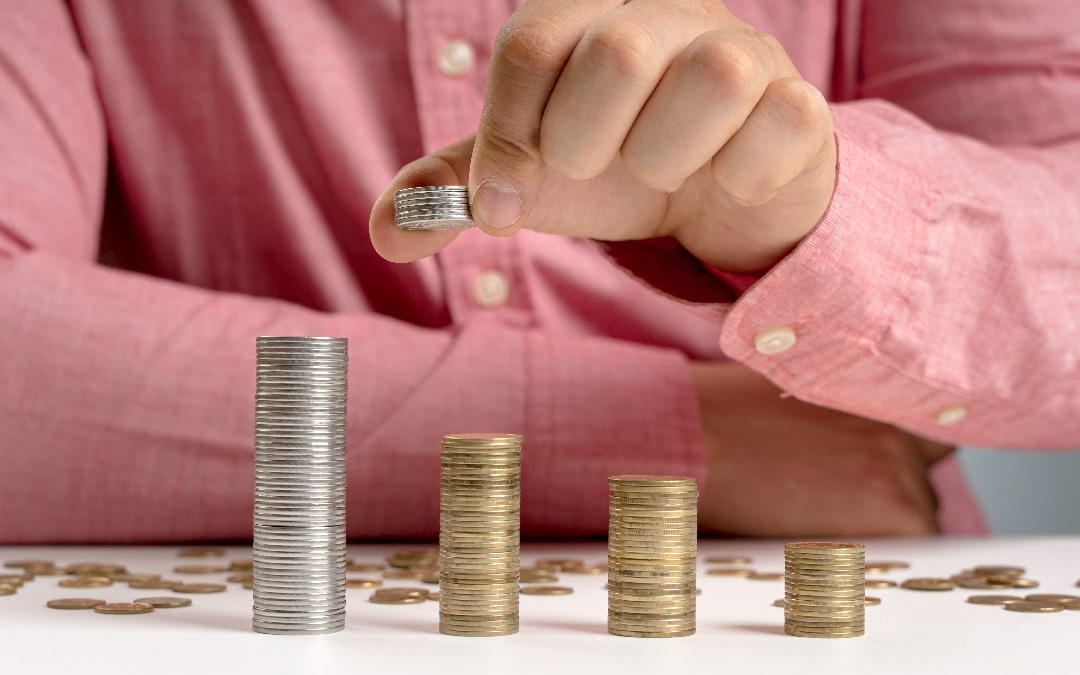
Retirement planning requires efficient risk management to help your investment portfolio grow and achieve financial goals.
At 140 million seniors in India account for about 12 per cent of our total population. This number is estimated to more than double to over 330 million by 2050. To put things in perspective the population of the USA is approx. 330 million now. With a falling birth rate, the share of seniors is also likely to grow to 22 per cent of India’s population. Also, over the years, with India’s progress towards becoming a developed economy, life expectancy has increased from 32 years in 1947 to 76 years. With increasing longevity, it is vital to make everyone realise that they need to start their financial planning early, ideally from the age of 40 years onwards. Starting early will ensure they can help secure financial independence to take care of their increasing medical expenses without sacrificing their lifestyle.
On retirement, regular income stops. This makes seniors look for investments that can offer higher returns to compensate for the loss of regular cash flow. This makes them vulnerable as they end up chasing high-return schemes without assessing the fundamental capital protection risk. In recent times, take the instances of PMC Bank or even Yes Bank, where many have had to sacrifice substantial sums out of their golden nest for the lure of higher returns. Instead of taking higher risks, there are other ways by which technology can help seniors increase their returns. For example, opting to invest directly in mutual funds either via the online platform of respective mutual funds or platforms of intermediaries such as Zerodha or Paytm Money provides an opportunity to save on the commission and earn more.
For retirement planning, it is recommended to adopt goal-based investment strategies which prioritise both the preservation of capital and the generation of sufficient income to support their lifestyle. Designing an effective investment portfolio requires careful consideration of various risks, such as liquidity and financial risks. This article attempts to present a practical framework that presents various alternatives seniors can consider as they plan to optimise returns while mitigating risks in their investment portfolios.
Key factors to consider.
Retirement planning must focus on the following primary goals:
- Capital Preservation: Protecting the principal amount from significant losses and higher returns that help generate a healthy cash flow and maintain your lifestyle must be weighed against the risk of losing your principal itself. Keeping money with high returns offered by unregulated entities like chit funds or via recommendations for investment in crypto-like instruments in WhatsApp groups must be evaluated against the fundamental need for capital preservation.
- Income Generation: Ensuring a steady stream of income to cover living expenses is essential to ensure you are not required to cringe on your lifestyle while keeping large sums invested in not assets like gold or yet-to-be-developed real estate.
- Growth Potential: Maintaining some growth to counteract inflation- the return on investment must be higher than the inflation rate to ensure a “real return.”
LIFE-TIME – A Six-Point Risk Framework
Achieving capital preservation, income generation, and growth goals requires a balanced approach. I have designed a LIFE-TIME framework that addresses six unique risks seniors need to consider: liquidity, Inflation, Financial Evaluation, Tax considerations, Income generation, and the need to Maintain the Estate.
1. Liquidity Risks
Liquidity risk refers to the potential difficulty of converting investments into cash without significant loss. For seniors, liquidity is crucial for covering unexpected expenses, such as medical bills or home repairs.
Strategies to Mitigate Liquidity Risks:
- Emergency Fund: Maintain an emergency fund with 6-12 months of living expenses in a highly liquid account, such as a savings account or a liquid mutual fund.
- Diversified Investment Vehicles: Include a mix of liquid assets (e.g., cash, fixed deposits) and less liquid investments (e.g., real estate, PPF) in the portfolio.
- Staggered Maturities: For fixed-income investments, consider laddering fixed or recurring deposits to ensure that some assets mature regularly, providing ongoing liquidity.
2. Financial Risks
Financial risks encompass a variety of factors, including market volatility, interest rate changes, and credit risk. These can significantly impact the returns and stability of a retirement portfolio.
Strategies to Mitigate Financial Risks:
- Asset Allocation:A. Equities: While stocks offer growth potential, they are also more volatile. Seniors should consider a lower allocation to equities, focusing on blue-chip stocks which provide dividends and some growth.B. Fixed Income: Bonds and debt funds are typically less volatile and provide regular income. However, interest rate changes can affect their value. To manage this risk, diversify across different bond types and maturities.C. Alternative Investments: Real estate, gold, or mutual funds can provide diversification benefits but should be cautiously approached due to their complexity and potential illiquidity.
- Risk Tolerance Assessment: Regularly reassess your risk tolerance. As you age, your capacity to recover from financial setbacks decreases, necessitating a more conservative approach.
- Regular Portfolio Review: Conduct annual reviews to rebalance the portfolio, ensuring it aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Adjust asset allocation as needed based on market conditions and changes in personal circumstances.
3. Income Generation and Inflation Protection
Generating income and protecting against inflation are critical components of a retirement portfolio. Traditional income sources, such as pensions and Provident Fund, may not be sufficient.
Strategies for Income Generation:
- Dividend Stocks: Invest in high-quality, dividend-paying stocks which offer a regular income stream and potential for capital appreciation.
- Fixed-Income Securities: Include government bonds, corporate bonds, and debt mutual funds to provide steady income.
- Real Estate Investment: Rental income from property can offer attractive yields and some protection against inflation.
4. Inflation Protection
- Inflation-Indexed Bonds: These bonds adjust their principal value based on inflation, providing a hedge against rising prices.
- National Pension Scheme (NPS): NPS offers market-linked growth and regular income post-retirement, adjusting for inflation.
- Diversified Equity Exposure: While more volatile, equities generally outpace inflation over the long term, providing growth potential that helps maintain purchasing power.
5. Tax Considerations
Taxes can significantly affect the net returns of your investment portfolio. Efficient tax planning is essential to maximise after-tax income.
Tax-Efficient Strategies:
- Tax-Deferred Accounts: Utilise retirement accounts such as PPF and NPS to defer taxes on investment gains until withdrawals are made.
- Tax-Free Accounts: Consider options like Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana and Senior Citizen Savings Scheme for tax-free growth and withdrawals, which can be advantageous for long-term planning.
- Asset Location: Place less tax-efficient investments (e.g., bonds, real estate) in tax-advantaged accounts and more tax-efficient investments (e.g., individual stocks) in taxable accounts.
6. Estate Planning and Legacy Goals
Many seniors have goals beyond their lifetime, such as leaving a legacy for their heirs or supporting charitable causes. Proper estate planning ensures these goals are met efficiently.
Key Considerations:
- Beneficiary Designations: Regularly update beneficiary designations on retirement accounts and insurance policies to reflect current wishes.
- Trusts and Wills: Establish trusts and wills to manage the distribution of assets according to your preferences and minimise estate taxes.
- Charitable Giving: Explore options such as charitable remainder trusts or donor-advised funds to support philanthropic goals while receiving potential tax benefits.
Conclusion
Designing an investment portfolio for seniors involves balancing the need for income and growth with the necessity of risk management. LIFE-TIME framework helps understand and address liquidity risks, financial risks, income generation, inflation protection, tax considerations, and estate planning; seniors can optimise their portfolios to achieve a secure and comfortable retirement. Regular reviews and adjustments ensure the portfolio aligns with changing goals and market conditions. With careful planning and a disciplined approach, seniors can enjoy financial stability and peace of mind in their golden years.
Written by Salil Datar for Outlook Money: Retirement